Extreme Heat and Humidity: A Growing Threat to Human Health
The impact of extreme heat and humidity on human health is becoming an increasingly urgent concern as the world experiences record-breaking temperatures and heat waves. In recent years, the frequency and severity of heat waves have intensified, leading to a range of health risks and even fatalities in various parts of the globe. From the scorching temperatures during the Hajj pilgrimage in Saudi Arabia to the heat-related deaths in countries like the US, Thailand, India, and Mexico, extreme heat is proving to be a deadly force.
Causes of Extreme Heat and Humidity
The primary cause of extreme heat and humidity can be attributed to climate change. With 2024 on track to be the warmest year ever recorded, the effects of global warming are becoming more evident. Heat waves are occurring more frequently, arriving earlier than anticipated, and lasting longer. When high temperatures are combined with elevated levels of humidity, the impact on human health becomes even more severe.
Impact on Human Health
One of the most significant dangers of extreme heat is dehydration. In high temperatures, the risk of dehydration increases, which can lead to serious health issues such as heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, heat can exacerbate breathing problems, especially in areas with high levels of pollution. Heat stress can also make it more challenging for people to work, increasing the likelihood of injuries.
Heat-related fatalities are a significant concern, with many deaths going uncounted each year. In 2023, Europe experienced over 47,000 heat-related deaths, underscoring the deadly consequences of extreme heat. Women and seniors have been identified as the populations most vulnerable to extremely hot weather, highlighting the importance of targeted interventions to protect these groups.
Measurement of Extreme Heat
Forecasters are increasingly using measures of heat stress and discomfort, such as the humidex, heat index, and apparent temperature, to assess the health risks associated with high temperatures. The “wet-bulb” temperature is a crucial metric that accounts for the effects of humidity on the body’s ability to cool itself through sweating. As humidity levels rise, the risk of heatstroke increases, even for healthy individuals with access to shade and water.
Wet-bulb temperatures are measured using electronic instruments at weather stations, with satellite data from sources like NASA and the International Space Station providing further insights into hot spots. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the US has developed advanced metrics like the wet-bulb globe temperature, which considers factors like wind speed, sun angle, and cloud cover in assessing heat stress.
Global Impact of Extreme Heat
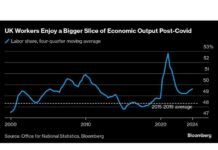
Traditionally, regions in South Asia and subtropical climates have experienced the highest levels of heat and humidity. However, with planetary warming and the influence of the El Nino weather pattern, extreme temperatures are now being recorded across a broader swath of regions, including parts of the US, Africa, India, Australia, and South America. Even typically temperate regions like the UK and Europe are experiencing record-breaking heat waves, underscoring the global reach of extreme heat events.
Economic Consequences of Extreme Heat
The economic impact of extreme heat extends beyond health concerns to affect various aspects of daily life. In cities, inequalities become more acute during heatwaves, while cooler regions experience higher food and energy prices. Supply chain disruptions, like the surge in coffee prices due to heat and drought in Vietnam, highlight the ripple effects of extreme heat on global markets. Power consumption rises during peak heat, leading to strain on the grid and increased prices for consumers.
Climate Change and Extreme Heat
The connection between extreme heat events and climate change is well-established, with global warming directly linked to the intensity and frequency of heat waves. Climate change also contributes to other weather extremes, such as wildfires and intense tropical storms. The impact of climate change on extreme heat is evident in regions like the western US, Australia, and India, where wildfires and heatwaves have become more frequent and severe.
Conclusion
As extreme heat and humidity continue to pose a significant threat to human health and well-being, it is crucial for policymakers, communities, and individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate the impact of heatwaves. By addressing the root causes of extreme heat through sustainable practices and climate action, we can work towards creating a safer and more resilient future for all.