California Fast Food Restaurants Facing Challenges After State Minimum Wage Hike
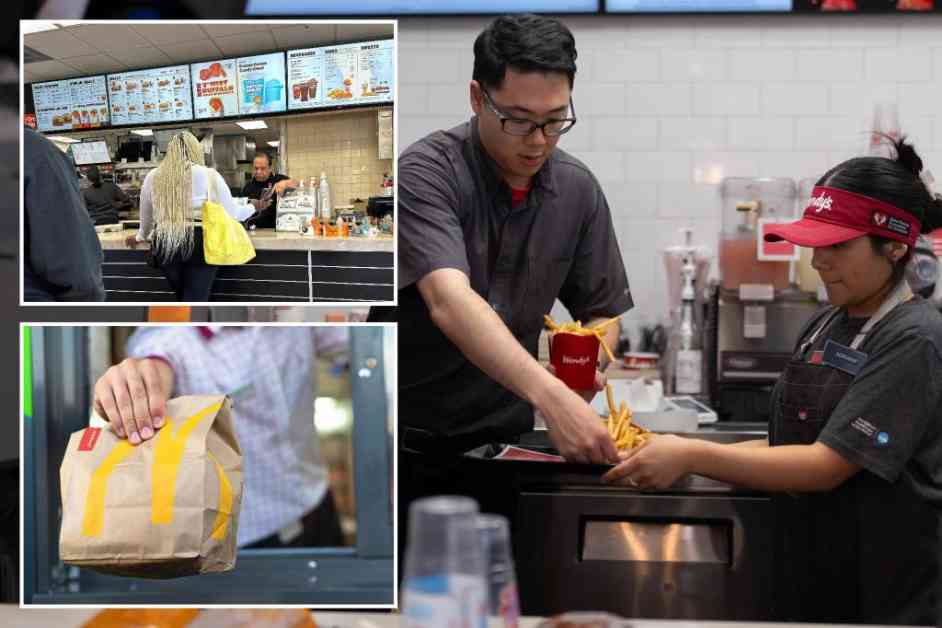
California fast food restaurants have been grappling with significant changes in response to the state’s new $20-an-hour minimum wage law. A recent survey conducted by the Employment Policies Institute revealed that 98% of fast food establishments in the Golden State have raised menu prices, while nearly 90% have reduced employee hours. These shifts in the industry come after the law was signed by Democratic Governor Gavin Newsom and went into effect on April 1.
Survey Findings and Impact on Businesses
The survey, which polled 182 fast food restaurant operators, highlighted the widespread effects of the minimum wage hike on the industry. According to the study, not only have almost all the restaurants increased their prices, but a staggering 93% plan to do so again next year. Additionally, 87% of establishments anticipate cutting employee hours within the next 12 months, a slight decrease from the 89% that implemented hour reductions this year.
Furthermore, the study revealed that 73% of fast food locations have reduced employee shift pick-up or overtime opportunities, while 70% have either cut staff or consolidated positions. These operational adjustments have been necessary for many restaurants to navigate the financial challenges posed by the higher minimum wage.
Rebekah Paxton, the research director at the Employment Policies Institute, expressed concerns about the negative impact of the wage increase on the fast food industry. She stated, “Even before the $20 wage went into effect, fast food restaurants made it clear they would not be able to survive. Now after just a few months, the policy has been a disaster, killing jobs and shuttering restaurants.”
Financial Strain and Future Expansion
The financial strain caused by the new minimum wage law is evident in the survey findings. Two-thirds of respondents indicated that the law would cost their restaurant at least $100,000 per location, while a quarter expected a $200,000 hit to their bottom line at each site. Additionally, when asked about the likelihood of expanding in California, 73% of restaurant operators said the new law would make them “significantly less likely” to grow in the state.
Moreover, the survey highlighted a concerning trend, with 74% of respondents expressing a greater likelihood of shutting down their restaurants in response to the challenges posed by the minimum wage increase. The closure of beloved chains like Rubio’s California Grill, which shuttered 48 locations due to the “rising cost of doing business,” underscores the significant impact of the policy on the fast food industry.
Response from Governor Newsom’s Office
In response to the survey findings, a spokesperson for Governor Newsom dismissed the results as a “bogus online survey conducted by a DC lobbying firm that’s funded by corporate restaurant chains.” The spokesperson emphasized that federal government data indicates an increase in fast food jobs in California since the minimum wage hike, contradicting the negative implications highlighted in the survey.
Fast Food Workers Union Demands
Despite the challenges faced by fast food restaurants, workers in the state have been advocating for further wage increases. The California Fast Food Workers Union, a branch of the Service Employees International Union (SEIU), recently presented a list of demands at the inaugural meeting of the state’s Fast Food Council. The union is calling for wages to be raised to $20.70 per hour by January 1, 2025, citing the need to keep up with the rising cost of living.
Impact on Popular Chains and Foot Traffic
The implementation of the $20-an-hour minimum wage law has had repercussions on popular fast food chains in California. According to a report by analytics firm Placer.ai, visits to establishments such as McDonald’s, Wendy’s, Burger King, In-N-Out Burger, and Jack in the Box have declined since April 1. Foot traffic at Burger King fell by 3.86%, Wendy’s by 3.24%, McDonald’s by 2.5%, In-N-Out Burger by 2.59%, and Jack in the Box by 0.8%.
Despite the challenges faced by the fast food industry in California, the debate over minimum wage policies and their impact on businesses and workers continues to be a contentious issue. As restaurant operators navigate the financial implications of the wage hike, the future of the industry remains uncertain in the face of ongoing economic changes.