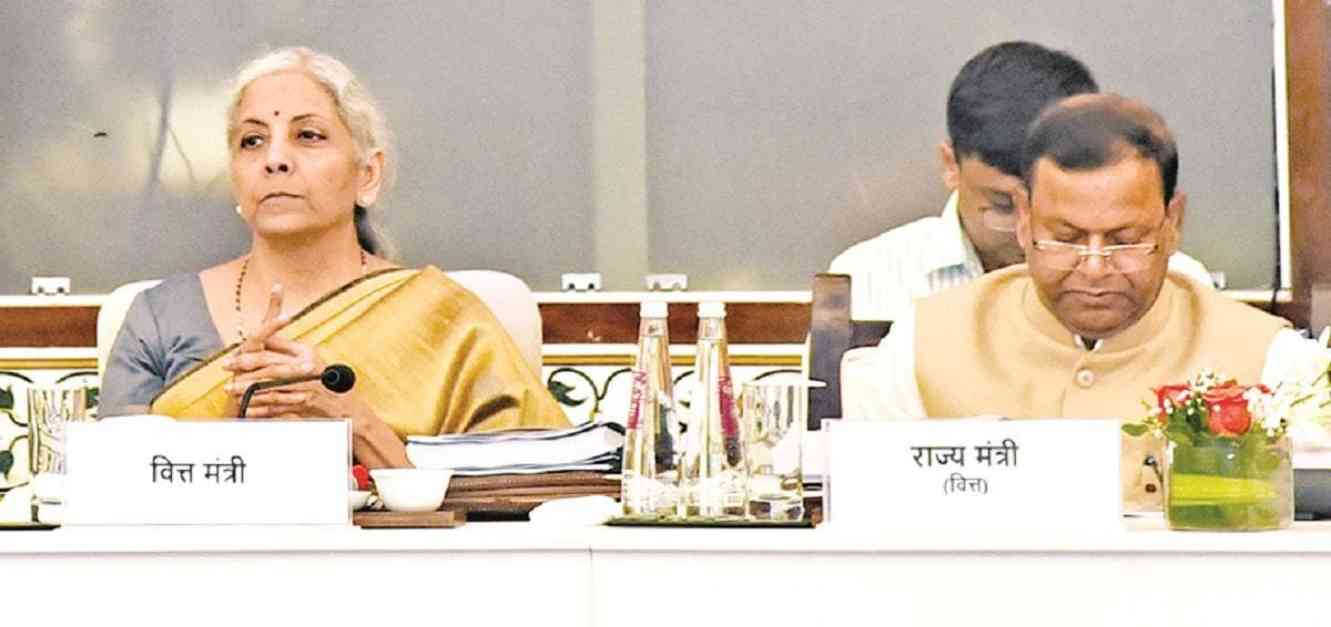
The 54th meeting of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council was a crucial one, with key decisions made to address pressing issues related to rate cuts, slabs, and compensation cess. The challenge ahead for the council will be to rationalize rates and adjust the part currently collected as cess in a manner that enhances the efficiency of the GST system and contributes to overall tax collection improvement.
One of the significant decisions taken by the Council was to exempt the import of services by foreign airlines from related parties based outside the country when such transitions are made without consideration. This move will provide relief to numerous foreign airlines that were previously served tax notices, easing their financial burden and enabling smoother operations.
Additionally, the Council recommended the implementation of business-to-consumer e-invoicing on a pilot basis. This decision follows the successful adoption of business-to-business e-invoicing, showcasing the Council’s commitment to leveraging technology to streamline tax processes and enhance compliance.
Subheadings:
Challenges in Rationalizing Rates and Cess
As the GST Council navigates key decisions regarding rate cuts, slabs, and compensation cess, one of the primary challenges lies in rationalizing rates to create a more coherent tax structure. Currently, the GST system comprises multiple tax slabs, leading to complexity and potential confusion among taxpayers. By streamlining rates and eliminating unnecessary distinctions, the Council aims to simplify the tax regime and make it more business-friendly.
Moreover, the Council must address the issue of compensation cess, which was introduced to compensate states for any revenue losses arising from the implementation of GST. Over time, the need for compensation cess has increased, necessitating a reevaluation of its structure and utilization. By reallocating cess collections and ensuring their optimal utilization, the Council can enhance the effectiveness of the GST system and ensure sustainable revenue generation.
Implications of Exempting Foreign Airlines from Tax Notices
The decision to exempt the import of services by foreign airlines from related parties located outside the country without consideration carries significant implications for the aviation industry. Previously, foreign airlines faced tax notices that added to their operational costs and created regulatory hurdles. With this exemption, foreign airlines can now conduct business more efficiently and focus on providing quality services to passengers.
Furthermore, the exemption reflects the Council’s commitment to fostering a conducive business environment for international players and promoting cross-border collaborations. By eliminating tax barriers for foreign airlines, the Council paves the way for enhanced trade relations and economic growth in the aviation sector.
Advancing Towards E-Invoicing for Enhanced Compliance
The Council’s decision to implement business-to-consumer e-invoicing on a pilot basis signifies a significant step towards enhancing compliance and leveraging technology in tax administration. E-invoicing has emerged as a powerful tool for simplifying invoice generation, improving accuracy, and reducing the risk of tax evasion. By extending e-invoicing to business-to-consumer transactions, the Council aims to streamline the invoicing process for small businesses and promote digitalization in tax compliance.
Moreover, the pilot implementation of e-invoicing will enable the Council to assess its effectiveness, identify potential challenges, and refine the system before full-scale implementation. This proactive approach underscores the Council’s commitment to embracing technological advancements and modernizing tax administration practices for the benefit of taxpayers and the economy.
In conclusion, the decisions taken by the GST Council at its 54th meeting underscore the commitment to addressing key issues related to rate cuts, slabs, and compensation cess. By rationalizing rates, exempting foreign airlines from tax notices, and advancing towards e-invoicing, the Council aims to enhance the efficiency of the GST system, promote compliance, and stimulate economic growth. As the Council continues to navigate complex tax reforms, stakeholders can expect further initiatives aimed at strengthening the tax regime and fostering a conducive business environment.