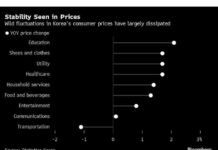
Spain’s Inflation Rate Drops to 2.9% in July
In a positive development for Spain’s economy, the country’s inflation rate dropped to 2.9% in July, according to final data released by the National Statistics Institute (INE) on Tuesday. This decrease marks a significant decline from the 3.6% inflation rate recorded in the previous month of June.
European Union-Harmonised Inflation
The 12-month European Union-harmonised inflation rate in Spain confirmed both the initial estimate and the predictions of analysts polled by Reuters, coming in at 2.9% for the month of July. This figure reflects a decrease from the previous month and aligns with expectations in the market.
It is worth noting that core inflation, which excludes volatile components such as fresh food and energy prices, also saw a decline in the 12-month period through July. The core inflation rate stood at 2.8%, down from 3% in the previous 12-month period ending in June, as reported by the INE.
National Consumer Prices
In addition to the European Union-harmonised inflation rate, Spain’s national consumer prices also experienced a decrease in July. Year-on-year, consumer prices fell by 2.8% in July, compared to a 3.4% decline in June. This data, released by the INE, confirms both the preliminary estimate released two weeks prior and the projections made by analysts surveyed by Reuters.
Overall, the latest inflation figures indicate a positive trend for Spain’s economy, with prices stabilizing and even decreasing in certain sectors. This can have a positive impact on consumers, as lower inflation rates may result in decreased cost of living and increased purchasing power.
Impact on the Economy
The drop in inflation rate can have various implications for Spain’s economy. A lower inflation rate indicates that prices are rising at a slower pace, which can be beneficial for consumers as it helps to maintain the purchasing power of their income. This can lead to increased consumer confidence and spending, which in turn can stimulate economic growth.
Furthermore, a decrease in inflation can also have an impact on interest rates and monetary policy. Central banks often use inflation rates as a key factor in determining their policy decisions, such as adjusting interest rates to control inflation. A lower inflation rate may signal that there is less pressure on the central bank to raise interest rates, which can be positive for businesses and borrowers.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, it will be important to monitor the inflation trends in Spain to assess the overall health of the economy. While a decrease in inflation can have positive effects, it is essential to ensure that it does not lead to deflation, which can be detrimental to economic growth.
Additionally, external factors such as global economic conditions, trade policies, and geopolitical events can also influence inflation rates in Spain. It is crucial for policymakers to remain vigilant and responsive to these factors to ensure economic stability and growth in the long term.
In conclusion, the drop in Spain’s inflation rate to 2.9% in July is a positive development for the country’s economy. This decrease, along with the stability in core inflation and national consumer prices, indicates a favorable trend that can benefit consumers and businesses alike. By closely monitoring inflation trends and responding proactively to economic challenges, Spain can continue on a path of sustainable growth and stability.