NASA Satellite Data Reveals Key Pollutant in National Environmental Justice Database
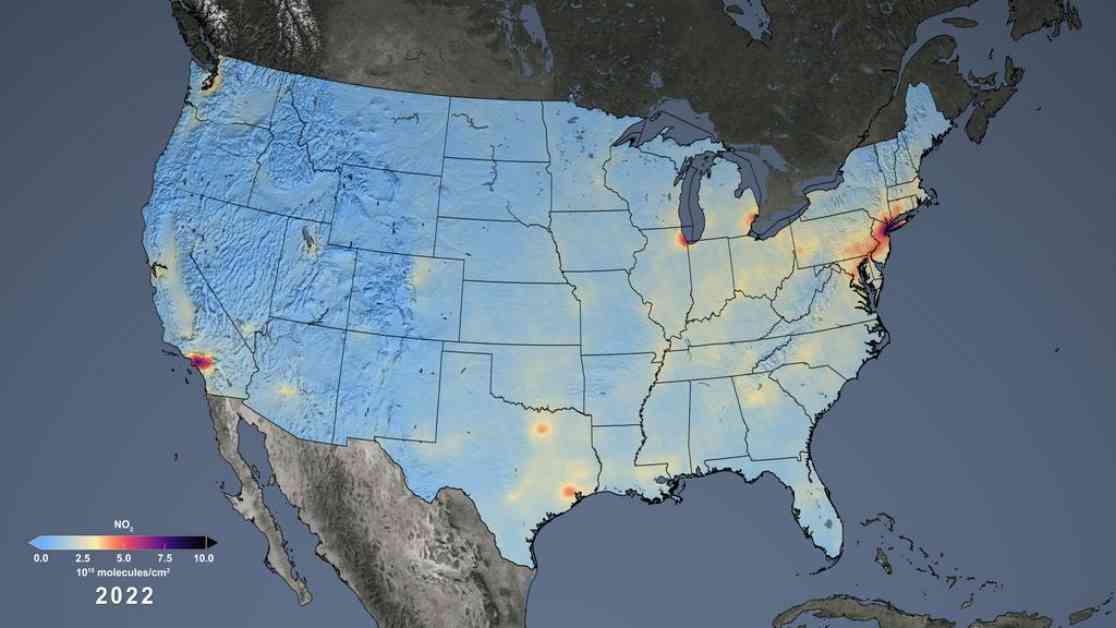
In a groundbreaking development, NASA recently announced the inclusion of nitrogen dioxide data from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on the Aura satellite into the Environmental Justice Screening and Mapping Tool (EJScreen). This move marks a significant advancement in monitoring air quality variations across the United States and identifying communities disproportionately affected by environmental hazards.
Nitrogen dioxide, a harmful air pollutant primarily emitted through the combustion of fossil fuels, has been a missing piece in the EJScreen database. The absence of this crucial data has hindered efforts to accurately assess the impact of air pollution on vulnerable populations and communities with higher environmental burdens. By integrating NASA’s satellite observations of nitrogen dioxide concentrations, environmental scientists and policymakers now have a more comprehensive understanding of the distribution of this harmful gas in the U.S.
The OMI instrument on NASA’s Aura satellite has been instrumental in providing detailed insights into Earth’s air quality for the past two decades. From its vantage point in space, OMI can detect nitrogen dioxide levels with remarkable precision, down to resolutions of 0.6 mile (1 kilometer). This high-resolution data was aggregated and analyzed by a collaborative team of scientists from NASA, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and three universities to create detailed maps showing nitrogen dioxide concentrations at the census block level.
By incorporating nitrogen dioxide data from NASA’s satellite observations into the latest version of EJScreen, users can now access color-coded maps that visually represent the distribution of this harmful pollutant across different regions in the U.S. This data visualization tool enhances the accessibility of critical environmental information and empowers individuals to advocate for improved air quality in their communities.
The Impact of Nitrogen Dioxide on Public Health
Nitrogen dioxide is known to have detrimental effects on public health, particularly on respiratory conditions such as asthma. Exposure to high levels of this pollutant can exacerbate respiratory ailments and contribute to the development of other health problems. By identifying areas with elevated nitrogen dioxide concentrations, policymakers and public health officials can target interventions to reduce exposure and improve air quality for at-risk populations.
Gaige Kerr, an air pollution researcher at George Washington University, emphasized the importance of democratizing access to high-quality nitrogen dioxide data. By integrating this information into the EJScreen tool, individuals without specialized expertise in data analysis or visualization can easily interpret the environmental impact of nitrogen dioxide in their communities. This enhanced transparency enables greater public engagement and advocacy for environmental justice initiatives.
Addressing Environmental Disparities through Data Visualization
The integration of NASA’s nitrogen dioxide data into the EJScreen database has significant implications for addressing environmental disparities in marginalized communities. By mapping out the distribution of this harmful pollutant at a granular level, researchers and policymakers can identify areas with disproportionately high levels of nitrogen dioxide and prioritize interventions to mitigate exposure risks.
Samuel Jordan, the president of the Baltimore Transit Equity Coalition, highlighted the value of accurate and localized nitrogen dioxide data in advocating for community health and well-being. By leveraging the insights provided by NASA’s satellite observations, organizations like the Baltimore Transit Equity Coalition can advocate more effectively for improved air quality standards and environmental justice initiatives in communities disproportionately impacted by pollution.
Transforming Environmental Monitoring with Satellite Data
The utilization of satellite data for environmental monitoring represents a transformative shift in how we assess and address environmental challenges. Tai Lung, an environmental protection specialist with the EPA, underscored the importance of NASA’s nitrogen dioxide data for screening and mapping disproportionate impacts in communities. The consistency and accuracy of satellite observations enable policymakers to make informed decisions and implement targeted interventions to reduce environmental disparities.
In December 2022, the EPA updated standards for heavy-duty trucks to reduce nitrogen oxide pollution by 80% starting in 2027. This regulatory action reflects a commitment to improving air quality and reducing harmful emissions from transportation sources. By implementing stringent emission standards for vehicles, policymakers aim to protect public health and mitigate the impact of nitrogen dioxide on vulnerable populations.
In conclusion, the integration of NASA’s nitrogen dioxide data into the EJScreen database represents a significant milestone in advancing environmental justice and public health initiatives. By harnessing the power of satellite technology, researchers and policymakers can gain valuable insights into air quality disparities and prioritize interventions to protect at-risk communities. This collaborative effort between NASA, the EPA, and academic institutions underscores the importance of data-driven decision-making in addressing environmental challenges and promoting equity in environmental protection.