In a recent turn of events, a unit of billionaire Mukesh Ambani-led Reliance Industries Ltd. is facing potential penalties for failing to establish a battery cell plant as part of India’s efforts to reduce import dependence. This move, which was a key component of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s initiative, has raised concerns about the company’s compliance with state-directed manufacturing goals. The repercussions of this failure could result in fines of up to 1.25 billion rupees ($14.3 million).
Reliance Faces Regulatory Scrutiny
Reliance New Energy Ltd., along with other companies, secured a bid for battery cell manufacturing in 2022 under the Indian government’s plan to incentivize local production. However, due to delays in setting up the plant, the company may now be subject to significant fines. Rajesh Exports Ltd., another participant in the government initiative, is also at risk of penalties for stalling the advanced-chemistry cell program. These fines, though relatively small in the grand scheme of things, highlight the challenges faced by companies in meeting state-mandated manufacturing targets.
While the fines may not pose a significant financial burden for Ambani’s conglomerate, they underscore the broader challenges in achieving Modi’s vision of boosting manufacturing in India. The country’s manufacturing sector has struggled to meet the ambitious goals set by the government, with the share of manufacturing in GDP falling from 15% in 2014 to 13% in 2023. This setback reflects the complex interplay of technological constraints and market dynamics that can impede efforts to bolster domestic manufacturing.
Challenges in the Manufacturing Landscape
The Production-Linked Incentives (PLI) program, designed to promote local manufacturing across various sectors, has yielded mixed results. While subsidies have successfully boosted the assembly of smartphones, other sectors, such as battery cell manufacturing for electric vehicles, have faced challenges in meeting production targets. Companies like Reliance New Energy, Rajesh Exports, and Ola Electric Mobility Ltd. were awarded bids to build battery cell plants as part of the PLI program, with subsidies totaling 181 billion rupees.
To qualify for these incentives, manufacturers were required to achieve specific milestones, including a minimum capacity commitment and local value addition targets. However, not all participants have been able to meet these requirements, leading to delays and potential penalties. Ola Cell Technologies Pvt., under Bhavish Aggarwal’s leadership, has made notable progress in its commitments under the PLI program, highlighting the varying success rates among participants.
Despite the challenges in the manufacturing landscape, there are promising developments on the horizon. Ola Electric, for instance, has made significant strides in its battery cell production plans and is on track to meet its timelines. This success underscores the importance of agile and adaptive strategies in navigating the complexities of the manufacturing sector.
Adapting to Changing Market Dynamics
In response to the shifting market dynamics and technological uncertainties, some companies, like Reliance Industries, have pivoted towards alternative energy sources, such as green hydrogen. This strategic shift reflects a broader trend in the industry towards sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions. However, challenges remain, particularly in the high capital investment required for lithium-ion battery plants.
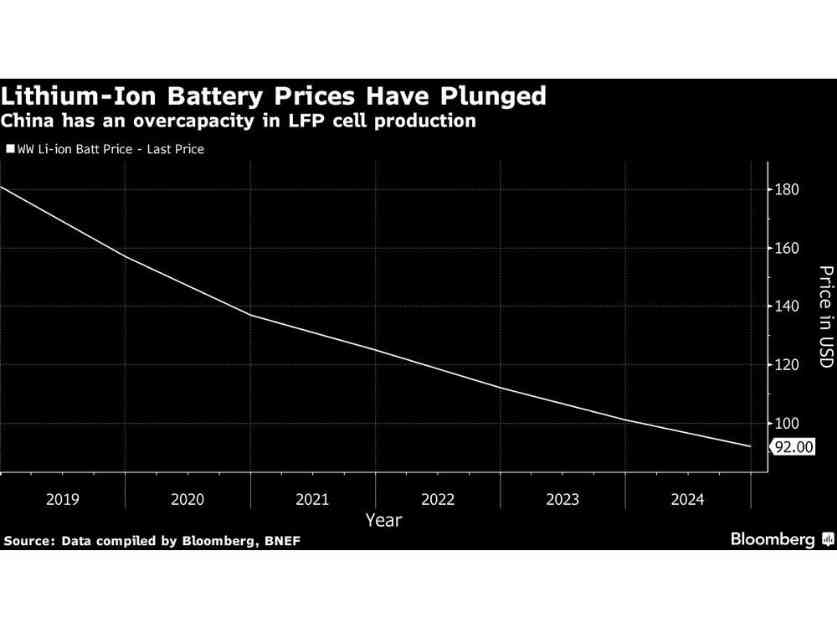
Jiayan Shi, an analyst at BloombergNEF, emphasized the risks associated with investing in cell manufacturing amid global market volatility and trade uncertainties. The declining prices of lithium-ion phosphate batteries have further exacerbated the challenges faced by domestic manufacturers, creating a competitive landscape that favors imports over local production. Despite these obstacles, companies like Reliance New Energy have made strategic acquisitions to bolster their capabilities in the battery sector.
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, companies will need to adopt innovative strategies and technologies to remain competitive in an increasingly globalized market. By addressing the challenges posed by regulatory requirements, technological constraints, and market dynamics, companies can position themselves for long-term success in the rapidly evolving manufacturing sector.