Florida Health Officials Discourage mRNA Covid Vaccines for Elderly and Vulnerable Residents
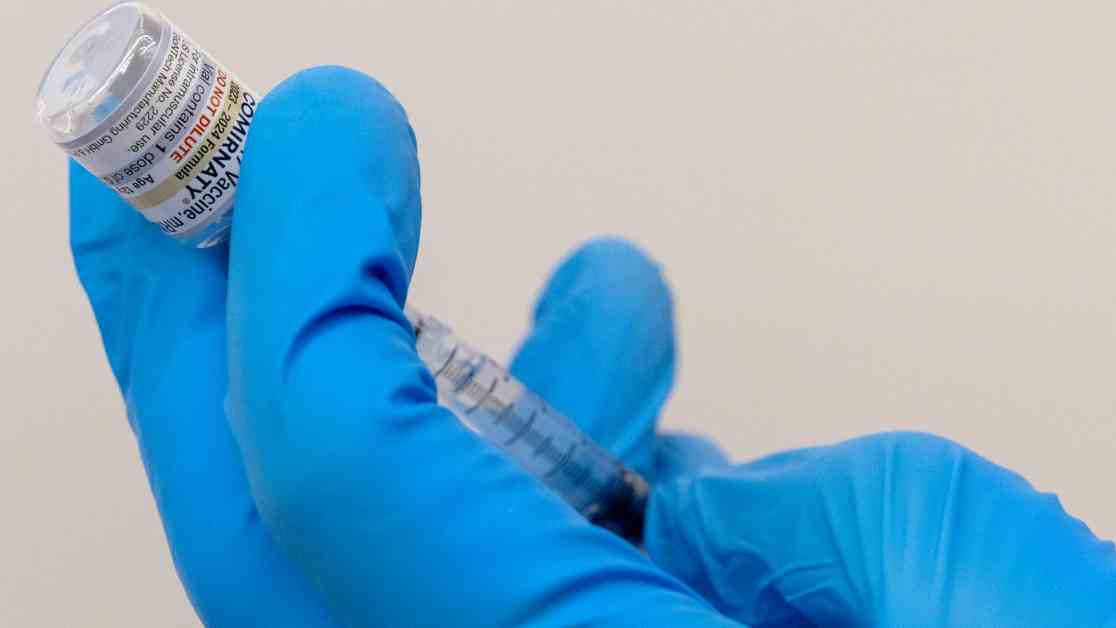
As the Covid-19 pandemic continues to impact communities across Florida, state health officials have once again raised concerns about the safety and effectiveness of mRNA Covid vaccines for the elderly and vulnerable populations. In updated guidance released recently, the Florida Health Department and state Surgeon General Joseph Ladapo advised health care providers to prioritize non-mRNA Covid-19 vaccines and treatment for patients over the age of 65 or with underlying health conditions.
Standing in contrast to recommendations from federal health agencies and medical experts, the Florida Health Department cited high rates of immunity from prior infections and “currently available data” as the basis for their advice against mRNA vaccines. The guidance highlighted safety concerns such as the risk of myocarditis, a rare heart condition, and POTS, a debilitating heart condition, associated with the mRNA vaccines from Pfizer and Moderna.
While studies have shown a small increased risk of myocarditis with the mRNA vaccines, particularly in young men, the overall benefits of vaccination in preventing severe Covid-19 outcomes far outweigh the risks. Research published in Nature Cardiovascular Research emphasized that individuals diagnosed with Covid-19 are five times more likely to develop POTS after infection compared to after vaccination, underscoring the importance of getting vaccinated.
Dr. Paul Offit, a vaccine expert at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, criticized the Florida surgeon general’s guidance as unnecessarily alarming, stating, “The mRNA vaccines are remarkably safe.” He emphasized the significantly higher likelihood of severe outcomes from Covid-19 for older adults compared to the minimal risks associated with vaccination.
New doses of the Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, specifically designed to target the KP.2 variant of the virus, have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and are expected to provide robust protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death. While Novavax offers an alternative non-mRNA vaccine option, experts stress the importance of vaccination for all eligible individuals to mitigate the spread of the virus.
Florida’s recommendation against mRNA vaccines has raised concerns among infectious disease specialists like Dr. Isaac Bogoch, who highlighted the potential risks for older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions. Despite a decline in Covid cases in some regions, the ongoing threat of the virus remains significant, particularly in high-risk populations.
As the CDC continues to recommend updated Covid vaccines for individuals aged 6 months and older, it is essential for healthcare providers to prioritize vaccination efforts for vulnerable populations. The availability of multiple vaccine options allows for tailored approaches to immunization, ensuring widespread protection against Covid-19.
Impact on Florida Nursing Homes and Vulnerable Populations
In Florida nursing homes, the resurgence of Covid infections following a decline from summer highs has raised concerns about the ongoing vulnerability of residents in long-term care facilities. Despite efforts to control the spread of the virus, the latest data from the CDC indicates a concerning uptick in Covid cases among nursing home residents.
The Florida Health Department’s recommendation against mRNA vaccines for the elderly and individuals with underlying health conditions has significant implications for the state’s vulnerable populations. By prioritizing non-mRNA vaccine options, healthcare providers must navigate the delicate balance between vaccine safety and efficacy in protecting those most at risk from severe Covid-19 outcomes.
In response to the evolving challenges posed by the pandemic, ongoing efforts to promote vaccination and preventive measures in nursing homes and other congregate settings are crucial to safeguarding residents and staff. The resurgence of Covid infections underscores the importance of maintaining vigilance and implementing robust infection control protocols to prevent outbreaks in vulnerable populations.
Subheadings:
The Importance of Vaccination for Vulnerable Populations
Risks and Benefits of mRNA Vaccines for Older Adults
Challenges in Mitigating Covid Spread in Nursing Homes
The Importance of Vaccination for Vulnerable Populations
Vaccination remains a critical tool in combating the spread of Covid-19, particularly among vulnerable populations such as older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions. Despite concerns raised by the Florida Health Department, experts emphasize the safety and efficacy of mRNA vaccines in preventing severe illness and hospitalization from Covid-19.
The risk of serious Covid infection and hospitalization for older adults far outweighs the minimal risks associated with vaccination, underscoring the importance of prioritizing immunization efforts for high-risk individuals. By adhering to CDC recommendations and promoting widespread vaccination, healthcare providers can help protect vulnerable populations from the devastating impacts of the virus.
Risks and Benefits of mRNA Vaccines for Older Adults
While concerns have been raised about the potential risks of myocarditis and POTS associated with mRNA vaccines, the overall benefits of immunization in preventing severe Covid-19 outcomes are well-documented. Studies have shown that the risk of myocarditis is significantly higher with a Covid infection than with vaccination, highlighting the importance of getting vaccinated to reduce the likelihood of severe cardiac complications.
In older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions, the benefits of mRNA vaccines in preventing hospitalization and death from Covid-19 far outweigh the risks of rare adverse events. By weighing the risks and benefits of vaccination, healthcare providers can make informed decisions to protect vulnerable populations from the impacts of the virus.
Challenges in Mitigating Covid Spread in Nursing Homes
The resurgence of Covid infections in Florida nursing homes underscores the ongoing challenges in mitigating the spread of the virus in congregate settings. Despite efforts to control outbreaks and implement infection control measures, the vulnerability of residents in long-term care facilities remains a significant concern.
By prioritizing vaccination and preventive measures in nursing homes, healthcare providers can help reduce the risk of Covid transmission and protect residents from severe outcomes. The availability of non-mRNA vaccine options provides additional flexibility in immunization strategies, allowing for tailored approaches to safeguarding vulnerable populations from the impacts of the virus.
In Conclusion
The Florida Health Department’s recommendation against mRNA vaccines for elderly and vulnerable residents has sparked debate among healthcare providers and experts about the best approach to protecting high-risk populations from Covid-19. While concerns about vaccine safety and efficacy persist, the overall benefits of immunization in preventing severe illness and hospitalization far outweigh the risks of rare adverse events.
As the pandemic continues to evolve, ongoing efforts to promote vaccination and preventive measures in nursing homes and other congregate settings are essential to safeguarding vulnerable populations from the impacts of the virus. By prioritizing immunization for high-risk individuals and implementing robust infection control protocols, healthcare providers can help mitigate the spread of Covid-19 and protect those most susceptible to severe outcomes.